For years, we have been working to improve the quality of service and speed up the production cycle. We receive inquiries about how our products are manufactured, and in order to bring this topic closer we have prepared a series of informative posts about our company’s production cycle.
The production cycle at Lubas is divided into 5 stages:
STAGE 1 DESIGN
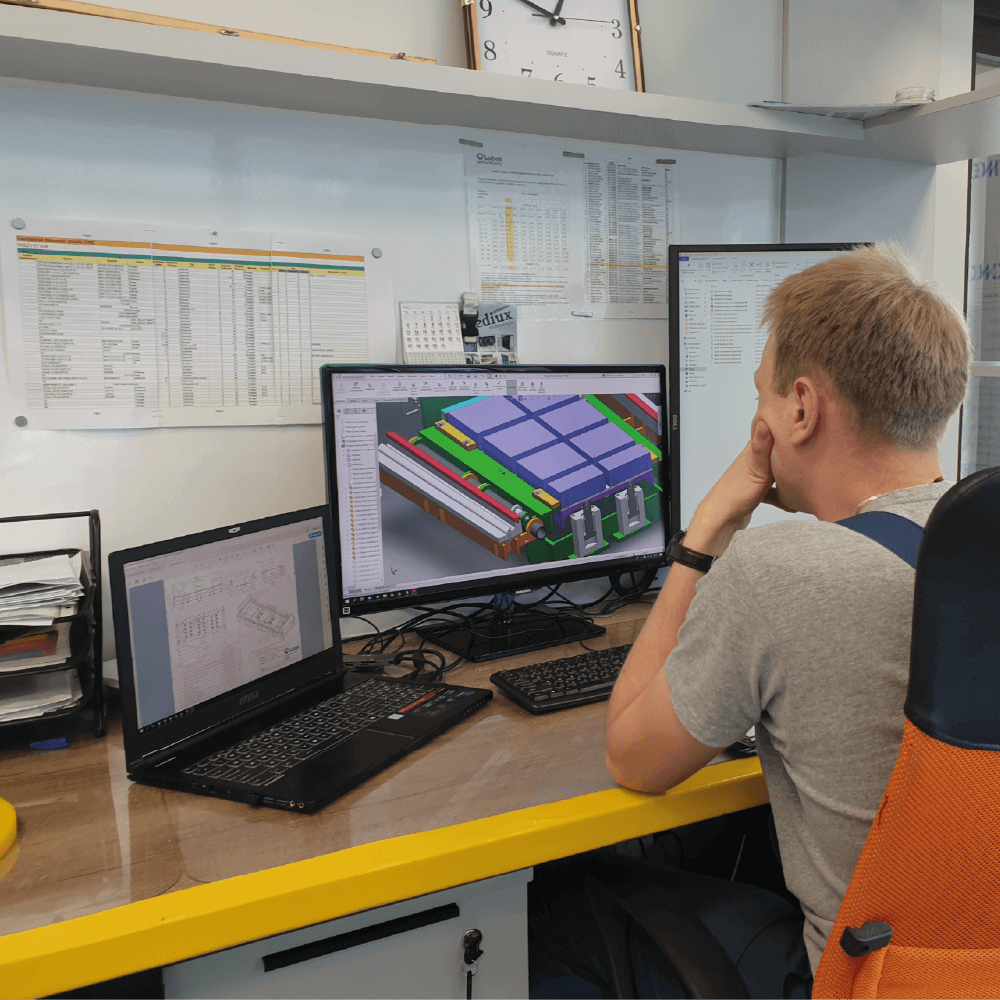 The first stage of the production cycle is to design a suitable mould. The dimensions, shape, hardness of the product, intended use and other parameters necessary for the execution of the order are agreed with the customer. Engineers then design a mould for the product starting by drawing a sketch in SolidWorks. The next step is forwarding the project to the CNC department, if it is an aluminum mould, or to the locksmith shop where steel moulds are assembled. Sometimes this stage is skipped provided both the design as well as the mould are prepared beforehand. Designing is an important phase because a well-designed mould guarantees that the demoulding process is fast and intuitive for foundry workers.
The first stage of the production cycle is to design a suitable mould. The dimensions, shape, hardness of the product, intended use and other parameters necessary for the execution of the order are agreed with the customer. Engineers then design a mould for the product starting by drawing a sketch in SolidWorks. The next step is forwarding the project to the CNC department, if it is an aluminum mould, or to the locksmith shop where steel moulds are assembled. Sometimes this stage is skipped provided both the design as well as the mould are prepared beforehand. Designing is an important phase because a well-designed mould guarantees that the demoulding process is fast and intuitive for foundry workers.
STAGE 2 ALUMINIUM MOULD MAKING
 When the design is ready, the created project documentation is forwarded to the CNC department. Aluminum moulds are prepared by operators of numerically controlled machines. Depending on the level of detail, the moulds can be either made of aluminum entirely or in part.
When the design is ready, the created project documentation is forwarded to the CNC department. Aluminum moulds are prepared by operators of numerically controlled machines. Depending on the level of detail, the moulds can be either made of aluminum entirely or in part.
STEEL MOULD MAKING
 Steel moulds are prepared according to the design and their manufacturing is carried out in the mechanical department. After the work is completed, the correctness of the dimensions and shape that the mould should have is verified so that it can move on to the next stage of production, which is the casting.
Steel moulds are prepared according to the design and their manufacturing is carried out in the mechanical department. After the work is completed, the correctness of the dimensions and shape that the mould should have is verified so that it can move on to the next stage of production, which is the casting.
STAGE 3 THE CASTING
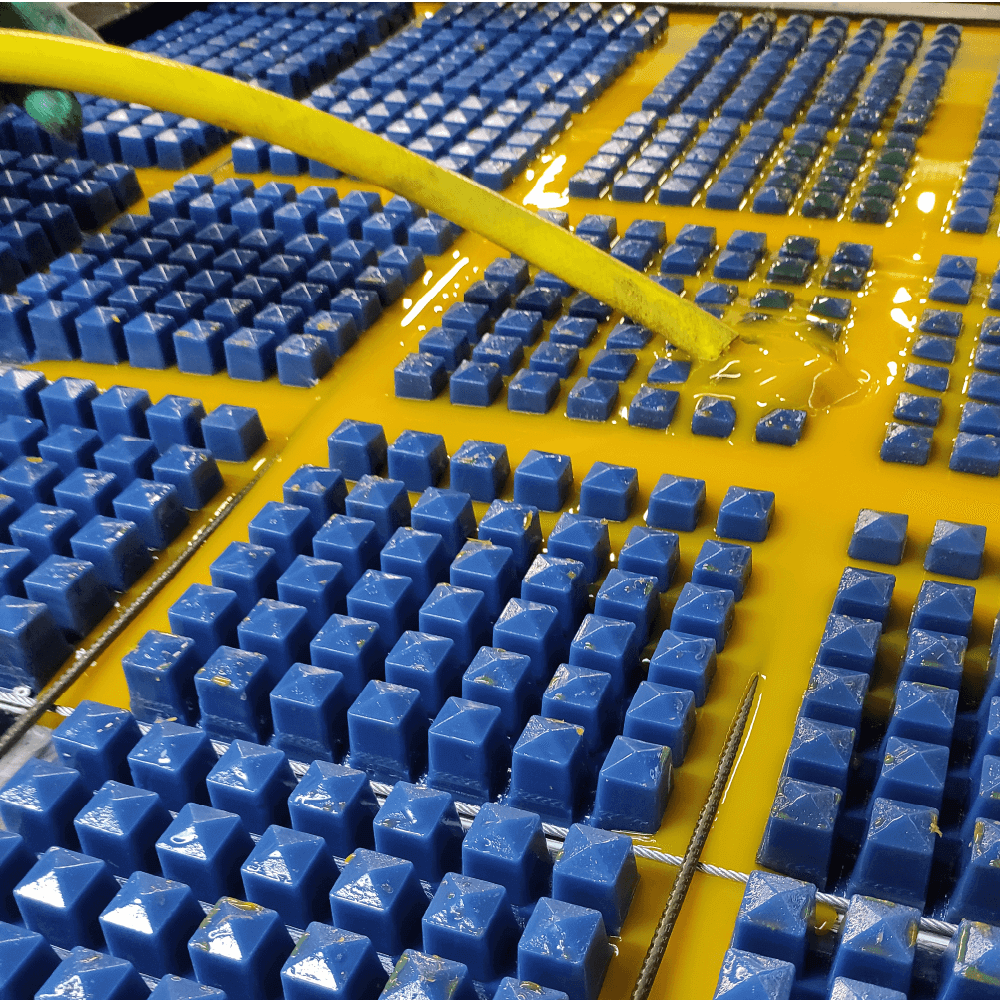 After the mould is ready, it is transferred a polyurethane elastomer foundry. Depending on the degree of product specificity, there are three possible types of casting: mould casting, ribbon casting and spray casting. An important element of the mould casting process is the temperature, both of the heating cabinet and the proper temperature of the mould itself. The most common method of casting is mould casting used in the manufacture of products such as screens or blades. Ribbon casting is used in the manufacturing products such as seamless sleeves and long pieces in the form of strips. Spray casting is typically used in round-shaped and geometrically complicated products.
After the mould is ready, it is transferred a polyurethane elastomer foundry. Depending on the degree of product specificity, there are three possible types of casting: mould casting, ribbon casting and spray casting. An important element of the mould casting process is the temperature, both of the heating cabinet and the proper temperature of the mould itself. The most common method of casting is mould casting used in the manufacture of products such as screens or blades. Ribbon casting is used in the manufacturing products such as seamless sleeves and long pieces in the form of strips. Spray casting is typically used in round-shaped and geometrically complicated products.
The prepared mould is lubricated with an anti-adhesive agent, and then it is transferred to the heating cabinet, where it is heated to the set temperature. After that, a specially prepared polyurethane compound is cast into the mould to give the target properties, hardness or colour. The mixture fixes and the cast product is ready to be demoulded. After demoulding, the product is once again put into the heating cabinet for 16-20 hours, it is annealed and then seasoned for several days to obtain full properties.
STAGE 4 PROCESSING
 Finishing works are the penultimate, extremely important, stage of the process affecting the visual effects of the product. Depending on the casting method, the products require different processes such as grinding, trimming, and/or removal of sub-fluids. The product prepared this way can be transferred to the finished products warehouse, where in the last stage it is packed and shipped.
Finishing works are the penultimate, extremely important, stage of the process affecting the visual effects of the product. Depending on the casting method, the products require different processes such as grinding, trimming, and/or removal of sub-fluids. The product prepared this way can be transferred to the finished products warehouse, where in the last stage it is packed and shipped.
STAGE 5 PACKING AND SHIPPING
 The logistics department is in charge of the finished goods warehouse from where domestic and international shipments are ordered. Goods in a variety of sizes, weights, and quantities are currently shipped to 42 countries across 6 different continents.
The logistics department is in charge of the finished goods warehouse from where domestic and international shipments are ordered. Goods in a variety of sizes, weights, and quantities are currently shipped to 42 countries across 6 different continents.






